Tumbleweed

Tumbleweed is a fork of Universal-Tween-Engine by Aurelien Ribon. To quote the parent project:
allows you to create smooth interpolations on every attribute from every object in your projects

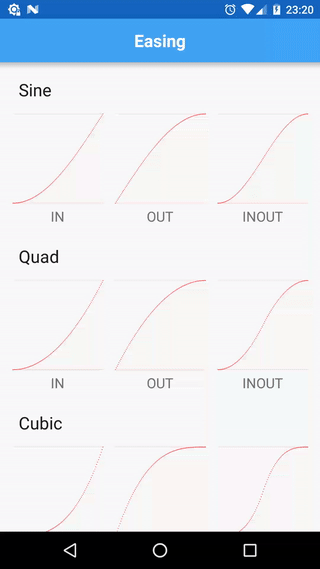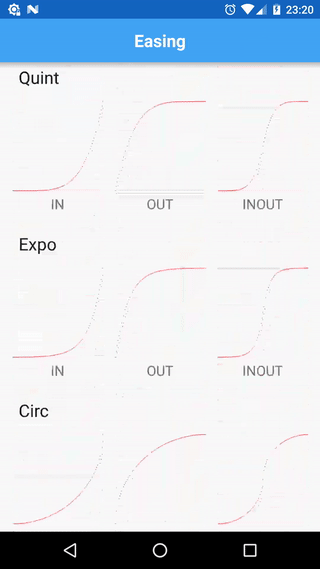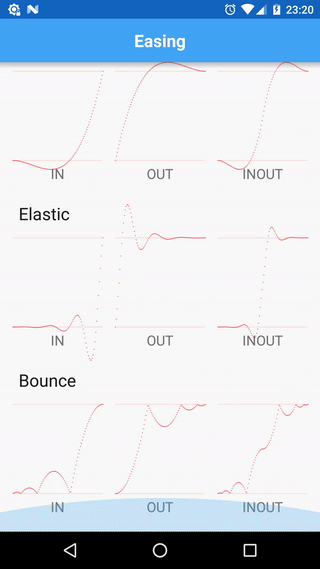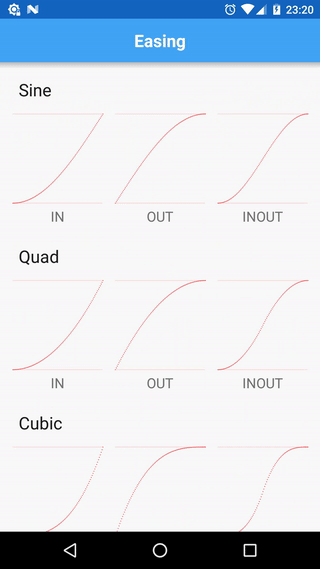
Tumbleweed comes with few changes and differences:
- decreased mutation of Tweens and Timelines (split definition and execution of tweens)
- encapsulated interpolation by introducing specific type (
TweenType<T>) - removed pooling (a constant source of unexpected behaviour)
- fixed
Circ.INequation - standalone module targeted on Android with a set of available TweenManagers for a
View,DrawableandHandler; a set of predefined interpolated types:color,alpha,translation,scale,rotation, etc; aTweenInterpolatorbridge in order to use equations with native AndroidAnimationandAnimator - some utility methods and helpers
// base java module
implementation 'io.noties:tumbleweed:${tumbleweed_version}'
// android module
implementation 'io.noties:tumbleweed-android:${tumbleweed_version}'
// kotlin extensions for android module
implementation 'io.noties:tumbleweed-android-kt:${tumbleweed_version}'
All modules have no external dependencies except for support-annotations
!!! Important notice for 2.0.0 version
Package name changed from
ru.noties.tumbleweed.*toio.noties.tumbleweed.*(regular find-n-replace can be used)Maven artifact group-id change to
io.noties
Usage
The API is pretty much the same:
final View view = findViewById(R.id.view);
Tween.to(view, Translation.XY, 2.F)
.target(0, 0)
.ease(Cubic.INOUT)
.start(ViewTweenManager.get(view));
Here Translation.XY is a predefined TweenType<View> (found in io.noties.tumbleweed.android.types.* package) that applies translation X and Y.
Cubic.INOUT is predefined equation (found in io.noties.tumbleweed.equations.*)
Please note that all durations are measured in seconds, so
2.Fis2 seconds
final View view = findViewById(R.id.view);
Timeline.createParallel()
.push(Tween.to(view, Alpha.VIEW, 2.F).target(.0F))
.push(Tween.to(view, Scale.XY, 2.F).target(.5F, .5F))
.start(ViewTweenManager.get(view));
With tumbleweed-android-kt Kotlin module the following usage is possible:
val view = findViewById<View>(R.id.view)
// `view.tweenManager` is an extension property for a view
// `startWhenReady` is an extension method to start configured tween
// when associated view has dimensions
view.tweenManager.startWhenReady {
// `this` is ViewTweenManager
this.killAll()
/*return */Timeline.createSequence()
// `then` extension method to push nested configured timeline
// `0.75F` is the default duration for tweens without duration specified
.then(Timeline.createParallel(0.75F)) {
// `with` extension method to configure tweens for a single target
with(view) {
to(Rotation.I).target(0.0F).ease(Bounce.OUT)
to(Argb.BACKGROUND).target(*Color.RED.toArgbArray())
}
// View has `tween` extension that expands to `Tween.to(view, /**/)`
push(view.tween(Alpha.VIEW).target(1.0F))
}
// repeat endlessly with 1 second delay between repeats
.repeat(-1, 1.0F)
}
Android predefined TweenTypes
io.noties.tumbleweed.android.types.*:
- Alpha.VIEW (applies alpha to a View:
view.setAlpha(..)). Range:0.0-1.0 - Alpha.DRAWABLE (
drawable.setAlpha(..), available for devices running KITKAT and up) Range:0.0-1.0 - Alpha.PAINT (
paint.setAlpha(..)). Range:0.0-1.0
- Argb.BACKGROUND (
view.setBackgroundColor(..)) - Argb.PAINT (
paint.setColor(..)) - Argb.TEXT_COLOR (
textView.setTextColor(..)) - Argb.STATUS_BAR (
window.setStatusBarColor(..), available for devices running Lollipop and up) - Argb.COLOR_DRAWABLE (
colorDrawable.setColor(..))
Argb also can be subclassed:
public class MyObjectArgb extends Argb<MyObject> {
@Override
protected int getColor(@NonNull MyObject myObject) {
return myObject.getColor();
}
@Override
protected void setColor(@NonNull MyObject myObject, int color) {
myObject.setColor(color);
}
}
Tween.to(myObject, new MyObjectArgb(), 2.F)
.target(Argb.toArray(0xFFff0000))
.start();
Please note that target color must be destructed to float[4] (argb values are interpolated individually). You can do it by calling: Argb.toArray(int) and Argb.toArray(int, float[])
- Elevation.I (
view.setElevation(), available for devices with Lollipop with up)
- Graphics.RECT (interpolates
left,top,rightandbottomof aRect) - Graphics.RECT_F (interpolates
left,top,rightandbottomof aRectF) - Graphics.POINT (interpolates
xandyof aPoint) - Graphics.POINT_F (interpolates
xandyof aPointF)
There is also special Graphics.points(List<PointF>) that creates interpolation for arbitrary list of PointF.
To receive a notification when rect or point have changed, the action method can be used:
final View view = getView(); // obtain some view
final int width = view.getWidth();
final int height = view.getHeight();
final Rect start = new Rect(0, 0, width, height);
final Rect target;
{
final int targetSide = Math.min(width, height) / 2;
final int left = (width - targetSide) / 2;
final int top = (height - targetSide) / 2;
target = new Rect(left, top, left + targetSide, top + targetSide);
}
Tween.to(start, Graphics.RECT, 2.F)
.target(target)
.action(view::setClipBounds)
.start(ViewTweenManager.create(view));
- Pivot.X (
view.setPivotX(..)) - Pivot.Y (
view.setPivotY(..)) - Pivot.XY (
view.setPivotX(..),view.setPivotY(..))
- Position.X (
view.setX(..)) - Position.Y (
view.setY(..)) - Position.Z (
view.setZ(..), available for devices running Lollipop and up) - Position.XY (
view.setX(..),view.setY(..)) - Position.XYZ (
view.setX(..),view.setY(..),view.setZ(..), available for devices running Lollipop and up)
- Rotation.I (
view.setRotation(..)) - Rotation.X (
view.setRotationX(..)) - Rotation.Y (
view.setRotationY(..)) - Rotation.XY (
view.setRotationX(..),view.setRotationY(..))
- Scale.X (
view.setScaleX(..)) - Scale.Y (
view.setScaleY(..)) - Scale.XY (
view.setScaleX(..),view.setScaleY(..))
- Scroll.X (
view.setScrollX(..)) - Scroll.Y (
view.setScrollY(..)) - Scroll.XY (
view.setScrollX(..),view.setScrollY(..))
- Translation.X (
view.setTranslationX(..)) - Translation.Y (
view.setTranslationY(..)) - Translation.Z (
view.setTranslationZ(..)available for devices running Lollipop and up) - Translation.XY (
view.setTranslationX(..),view.setTranslationY(..)) - Translation.XYZ (
view.setTranslationX(..),view.setTranslationY(..)andview.setTransaltionZ(..)available for devices running Lollipop and up)
These are just helpers and provided for faster iterations. They all implement the base TweenType<T> interface that is used by Tween:
public interface TweenType<T> {
int getValuesSize();
void getValues(@NonNull T t, @NonNull float[] values);
void setValues(@NonNull T t, @NonNull float[] values);
}
For example in case of Translation.XY:
@NonNull
public static final Translation XY = new TweenType<View>() {
@Override
public int getValuesSize() {
// we are interpolating x and y, so it's 2
//
// `getValues` and `setValues` methods will be called
// with an array of the returned size
return 2;
}
@Override
public void getValues(@NonNull View view, @NonNull float[] values) {
values[0] = view.getTranslationX();
values[1] = view.getTranslationY();
}
@Override
public void setValues(@NonNull View view, @NonNull float[] values) {
view.setTranslationX(values[0]);
view.setTranslationY(values[1]);
}
};
Android TweenManagers
ViewTweenManager
ViewTweenManager attaches to View draw cycle and invalidates it via view.postInvalidateOnAnimation(). It will be automatically disposed when a View to which it is attached to is detached from a window.
To obtain a ViewTweenManager call:
ViewTweenManager.get(view);
Normally you would want to ensure that a view has only one instance of a ViewTweenManager. Since version 2.0.0 ViewTweenManager does it automatically by caching created instance with View.setTag(int, Object) call.
Timeline.createSequence()
.push(Tween.to(view, Scale.XY, 0.4F).target(0.25F, 0.25F))
.push(Tween.to(view, Scale.XY, 0.4F).target(1.0F, 1.0F))
.start(ViewTweenManager.get(view));
ViewTweenManager will be automatically disposed when view is detached from a window.
DrawableTweenManager
DrawableTweenManager can be used with a Drawable (sample application heavily uses it).
To obtain an instance:
DrawableTweenManager.create(Drawable)DrawableTweenManager.create(Drawable, float)- the second argument is update interval (FPS), default one is:1.F / 60(all durations are in seconds), so equals to 60 frames per second.
In order to function correctly Drawable must be attached to a View or have manually set Drawable.Callback (internally uses invalidateSelf() and scheduleSelf())
HandlerTweenManager
HandlerTweenManager uses Handler as a dispatcher for update calls.
To obtain an instance:
HandlerTweenManager.create()- creates an instance with main thread Looper and 60 updates per second (60 FPS)HandlerTweenManager.create(float)- creates an instance with main thread Looper and specified update interval (in seconds, so1.F / 60would be equal to 60 FPS)HandlerTweenManager.create(float, Handler)- creates an instance with specified Handler and update interval (in seconds)
AnimatorTweenManager
In 2.0.0 version AnimatorTweenManager is added. It lets using Tumbleweed animations in Android-native way (for example in custom transitions):
@Override
public Animator createAnimator(ViewGroup sceneRoot, TransitionValues startValues, TransitionValues endValues) {
/*obtain transition values, validate their presence*/
final View v = endValues.view;
final AnimatorTweenManager tweenManager = AnimatorTweenManager.create();
Timeline.createSequence()
.push(Tween.to(v, Rotation.I, .25F).target(360))
.push(Tween.to(v, Scale.XY, .25F).target(.5F, .5F))
.push(Tween.to(v, Scale.XY, .25F).target(1, 1))
.start(tweenManager);
return tweenManager.animator();
}
Android Kotlin extensions
View
// obtain a ViewTweenManager
view.tweenManager // => ViewTweenManager.get(view)
// Tween.to(view, Alpha.VIEW, 0.25F)
view.tween(Alpha.VIEW, 0.25F)
// Tween.to(view, Alpha.VIEW), NB duration must be set explicitly
// via `duration(float)` method
view.tween(Alpha.VIEW)
// execute when view has dimensions
// will check if dimensions are present or register a OnPreDrawListener
view.whenReady {
view.width
}
// calculate position of a view relative to its parent
val point = view.relativeTo(parent)
Drawable
// create an instance of DrawableTweenManager
drawable.tweenManager() // => DrawableTweenManager.create()
// create an instance of DrawableTweenManager with
// specified update interval in seconds
drawable.tweenManager(1.0F / 120.0F)
// Tween.to(drawable, Alpha.DRAWABLE, 0.25F)
drawable.tween(Alpha.DRAWABLE, 0.25F)
// Tween.to(drawable, Alpha.DRAWABLE), NB to set duration
// explicitly via `duration(float)` method
drawable.tween(Alpha.DRAWABLE)
// apply intrinsic bounds
drawable.applyIntrinsicBounds()
// apply intrinsic bounds if current bounds are empty
drawable.applyIntrinsicBoundsIfEmpty()
TweenManager
// all tween managers
view.tweenManager.start {
Tween.to(view, Rotation.I, 0.4F).target(180.0F)
}
// view-tween-manager only
// start only after associated view has dimensions
view.tweenManager.startWhenReady {
Tween.to(view, Translation.Y, 0.75F).target(view.height / 2.0F)
}
Timeline
Timeline.createParallel()
// push nested timeline
.then(Timeline.createSequence()) {
push(Tween.to(view, Pivot.XY).target(0F, 0F))
push(Tween.to(view, Scale.XY).target(0.5F, 0.5F))
}
// configure tweens for a single target
.with(view) {
to(Pivot.XY).target(0F, 0F)
to(Scale.XY).target(0.5F, 0.5F)
}
Callbacks
Both Tween and Timeline has extensions for simplified callbacks addition:
onBegin- once tween has started (called only once)onStart- once tween started and on each repetition startonEnd- once tween completed and on each completion of repetitiononComplete- once tween has completed (called only once)
Tween.to(view, Alpha.VIEW, 0.5F)
.onBegin {
// tween started
}
.onComplete {
// tween completed
}
Duration
// Long: convert milliseconds to float seconds
1000L.toFloatSeconds() // => 1.0F
// Int: convert milliseconds to float seconds
450.toFloatSeconds() // => 0.45F
Argb
val color = Color.RED
// convert Int color to Argb array
color.toArgbArray()
// can be used like this:
// notice the _spread_ operator
Tween.to(view, Argb.BACKGROUND, 0.25F).target(*color.toArgbArray())
val array = Color.RED.toArgbArray()
// convert Argb float array to color
val color: Int = array.toColor()



