TreeView
Introduction: An Android TreeView with RecyclerView
Tags:
Maintainers Needed!See #12 for more details.
An TreeView implement in Android with RecyclerView written in kotlin.
Features
- 100% written in kotlin.
- Customise,
in the futureyou can implement your own tree data structure. - Fetching data asynchronously(Lazy load), no need to load all data at once.
- Horizontal scroll support.
(with bug) - Built-in DSL
Screenshot

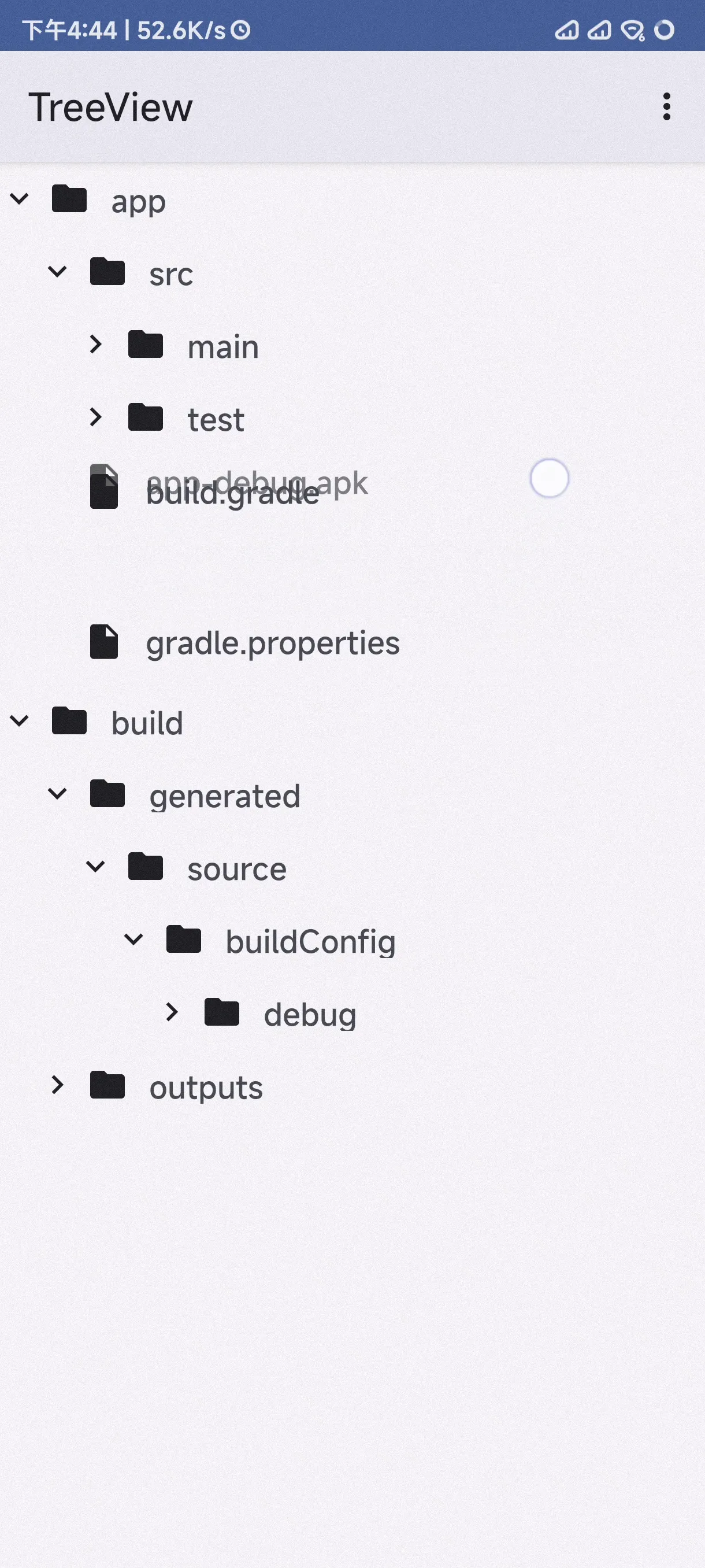
TODO
- Select or Deselect Node
- Better TreeNodeGenerator API
- More API to operate the node in the tree, such as expand, collapse, etc.
- Draggable nodes
Usage
- Add the dependency to your gradle file
implementation("io.github.dingyi222666:treeview:1.3.3")
- Use the
DataSourceDSL to create tree used for the TreeView. Also you can use theTreeNodeGeneratorto create the tree.
private fun createTree(): Tree<DataSource<String>> {
val dataCreator: CreateDataScope<String> = { _, _ -> UUID.randomUUID().toString() }
return buildTree(dataCreator) {
Branch("app") {
Branch("src") {
Branch("main") {
Branch("java") {
Branch("com.dingyi.treeview") {
Leaf("MainActivity.kt")
}
}
Branch("res") {
Branch("drawable") {
}
Branch("xml") {}
}
Leaf("AndroidManifest.xml")
}
}
}
}
}
Create a node binder to bind the node to the layout, and in most case also implement node click events in this class
Note: For the indentation setting of the item, we recommend using a Space widget placed at the visual leftmost of your item layout.
The width of this widget is the indentation width of the item.
inner class ViewBinder : TreeViewBinder<DataSource<String>>(),
TreeNodeEventListener<DataSource<String>> {
override fun createView(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): View {
return if (viewType == 1) {
ItemDirBinding.inflate(layoutInflater, parent, false).root
} else {
ItemFileBinding.inflate(layoutInflater, parent, false).root
}
}
override fun getItemViewType(node: TreeNode<DataSource<String>>): Int {
if (node.isChild) {
return 1
}
return 0
}
override fun bindView(
holder: TreeView.ViewHolder,
node: TreeNode<DataSource<String>>,
listener: TreeNodeEventListener<DataSource<String>>
) {
if (node.isChild) {
applyDir(holder, node)
} else {
applyFile(holder, node)
}
val itemView = holder.itemView.findViewById<Space>(R.id.space)
itemView.updateLayoutParams<ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams> {
width = node.depth * 22.dp
}
}
private fun applyFile(holder: TreeView.ViewHolder, node: TreeNode<DataSource<String>>) {
val binding = ItemFileBinding.bind(holder.itemView)
binding.tvName.text = node.name.toString()
}
private fun applyDir(holder: TreeView.ViewHolder, node: TreeNode<DataSource<String>>) {
val binding = ItemDirBinding.bind(holder.itemView)
binding.tvName.text = node.name.toString()
binding
.ivArrow
.animate()
.rotation(if (node.expand) 90f else 0f)
.setDuration(200)
.start()
}
override fun onClick(node: TreeNode<DataSource<String>>, holder: TreeView.ViewHolder) {
if (node.isChild) {
applyDir(holder, node)
} else {
Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Clicked ${node.name}", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()
}
}
override fun onToggle(
node: TreeNode<DataSource<String>>,
isExpand: Boolean,
holder: TreeView.ViewHolder
) {
applyDir(holder, node)
}
}
- If you want to implement horizontal scrolling, you need to set the
supportHorizontalScrollto true
treeview.supportHorizontalScroll = true
- Now you can create the tree structure and set up the node generator and node binder for the
TreeView, and then call
refresh()to load the data
val tree = createTree()
(binding.treeview as TreeView<DataSource<String>>).apply {
bindCoroutineScope(lifecycleScope)
this.tree = tree
binder = ViewBinder()
nodeEventListener = binder
}
lifecycleScope.launch {
binding.treeview.refresh()
}
If you want to load dynamic data (etc. local file), you can see this example here
Done! Enjoy using it.
Special thanks
- Rosemoe (Help improve the TreeView horizontal scrolling support)
- HackerMadCat/Multimap (Multimap implementation in kotlin)


